Automate NPM packages security fixes with recurring tasks on CI
When developing on Node.js, our team uses a lot open source NPM packages. Each of them has their own benefits and drawbacks that they bring to your project. In this article, we will discuss:
- Cost-free options for vulnerability testing NPM dependencies
- Drone CI configuration for running recurring checks
- Auto Pull Request creation with fixed packages
NPM audit and more
The first thing that comes to mind when we talk about vulnerability audits is the NPM audit tool. This tool uses a publicly available vulnerability catalog to check your project and propose library version updates to fix any issues discovered. You can read more in the official NPM blog here.
Another good, free report that still uses out-of-the-box available options is npm outdated. This report uses a command check registry to see if any installed packages are currently outdated. That information is not necessarily useful for day-to-day work, but good to know for the long term, so you’re less tempted to simply abandon a project.
$ npm outdatedPackage Current Wanted Latest Locationglob 5.0.15 5.0.15 6.0.1 test-outdated-outputnothingness 0.0.3 git git test-outdated-outputnpm 3.5.1 3.5.2 3.5.1 test-outdated-outputlocal-dev 0.0.3 linked linked test-outdated-outputonce 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.3 test-outdated-output
Automated npm outdated reports
These tools are very useful, but, of course, automated reports are even better. For this purpose, we use Drone CI (free and open source) and the new feature, Cron Jobs, to set recurring tasks. You’re free to use any other CI you like, however, which will probably support the same functionality. For those not familiar with Drone CI, read my Getting Started article here.
Since Drone CI supports multiple pipelines, each report has its own pipeline and does not affect the main one. For a wider look, check out the example here. In the meantime, let’s begin with npm outdated.
kind: pipelinename: npm outdatedsteps: - name: outdated image: node:10-alpine commands: - npm outdated - name: slack_notification image: plugins/slack settings: webhook: https://hooks.slack.com/services/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 template: > NPN detected outdated packages at *{{repo.name}}* for *{{build.branch}}* branch. Report available by the link {{build.link}} when: status: - failuretrigger: cron: [weekly]
We think the yaml syntax speaks well by itself. In the first step, we use node:10-alpine as a base image and run npm outdated. In the second step, a Slack notification is executed only if there is something to update(npm outdated exited with error exit code). To get the Slack webhook URL, visit this page
In the latest lines, the whole pipeline is triggered by the Cron Job labeled “outdated.” For our projects, we set that job for weekly execution, since we don’t plan to update packages everytime a new release comes.
To define the task in Drone, go to Project -> Settings.
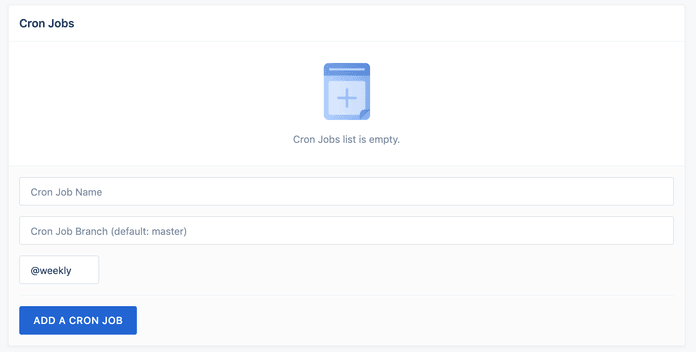
Through this interface, you can choose the name of the job (which is used for pipeline filtering), the branch and the interval, which can be hourly, daily, weekly, monthly or yearly.

Automated npm audit and fix PR creation
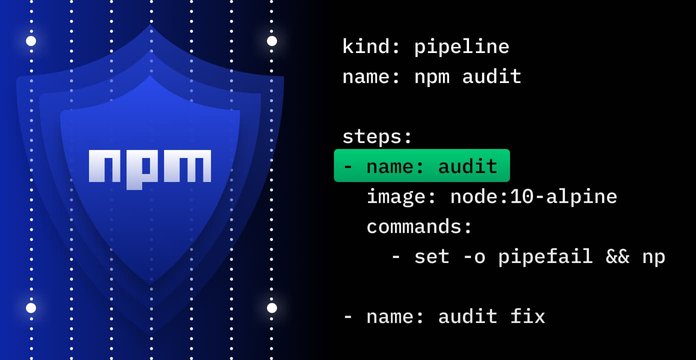
The npm audit command will check your app for vulnerabilities and update packages to any version current version where needed. The pipeline is very similar to the previous one, but with an extra step involving PR creation.
kind: pipelinename: npm auditsteps: - name: audit image: node:10-alpine commands: - set -o pipefail && npm audit --force 2>&1 | tee audit.log - name: audit fix image: node:10-alpine commands: - npm audit fix when: status: - failure - name: create_fix_pr image: lnikell/github-hub:2.11.2 environment: GITHUB_TOKEN: from_secret: github_token commands: - git config --global user.email "email@example.com" - git config --global user.name "example" - git checkout -b drone/npm-audit-fix-${DRONE_BUILD_NUMBER} - git add package.json package-lock.json - git commit -m 'npm audit fix' - git push origin drone/npm-audit-fix-${DRONE_BUILD_NUMBER} - hub pull-request -m "[Security] NPM Audit Fix" -m "$(cat audit.log | tail -2)" -m "${DRONE_BUILD_LINK}" when: status: - failure - name: slack_notification image: plugins/slack settings: webhook: https://hooks.slack.com/services/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 template: > NPN detected vulnerable packages at *{{repo.name}}* for *{{build.branch}}* branch. Report available by the link {{build.link}} when: status: - failure
In the first step, we use the same node:10-alpine image and run NPM audit. We also save an audit.log file containing the results in order to output to PR later. If vulnerable packages were found during the npm audit, the next step will fail, trigger the nmp audit fix process and pull request creation.
-name: audit fix image: node:10-alpine commands: - npm audit fix when: status: - failure
In order to create a pull request, we use hub – the command line tool for dealing with Github API. We need to generate a Github Personal Token to use it for an API call. Go to this page and create a new one
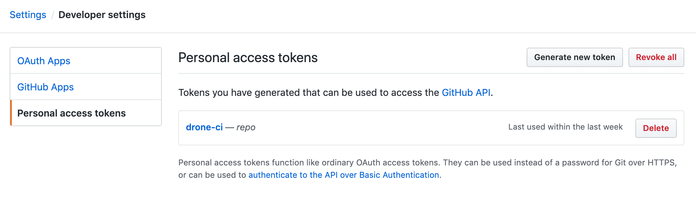
Select “repo” permissions scope, then add your generated token to secrets in Drone with the name “github_token”.
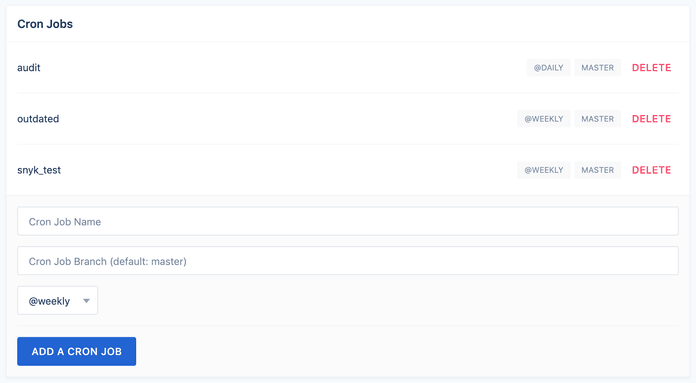
This is used as environment variable in the step below.
- name: create_fix_pr image: lnikell/github-hub:2.11.2 environment: GITHUB_TOKEN: from_secret: github_token commands: - git config --global user.email "lnikell@gmail.com" - git config --global user.name "drone" - git checkout -b drone/npm-audit-fix-${DRONE_BUILD_NUMBER} - git add package.json package-lock.json - git commit -m 'npm audit fix' - git push origin drone/npm-audit-fix-${DRONE_BUILD_NUMBER} - hub pull-request -m "[Security] NPM Audit Fix" -m "$(cat audit.log | tail -2)" -m "${DRONE_BUILD_LINK}" when: status: - failure
In this step, we declare the pattern for branch creation and create a pull request with the last two lines from the audit.log. This gives us a nice PR:
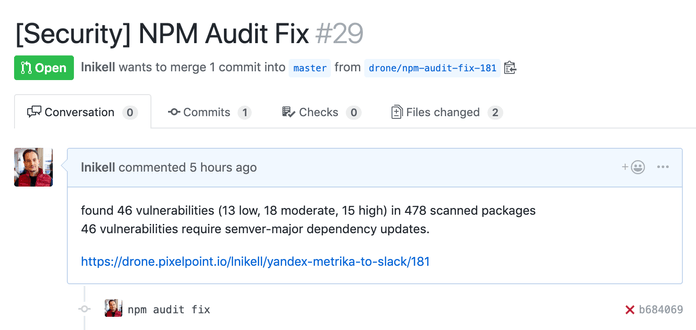
Finally, we need to look at the trigger part of the pipeline. Since you only want to execute those checks as a part of Cron job, you need to add the following:
trigger: cron: [name_of_the_job]
However, remember that you still need think about your main pipeline. To prevent it from running during the Cron tasks, you have to use the exclude option like this:
trigger: cron: exclude: [name_of_the_job]
See an example giving you a useful overview of all pipelines here.
Conclusion
That was just one example of how recurring tasks on CI can be useful to you for the purposes of building, testing and fixing. You only have to set up it once and you’ll be informed of the security of your project on a daily/weekly basis. The approach we use in our examples should be easily adaptable for Travis CI or Gitlab; if you do it this way, please share your pipeline here.